Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Healthcare: Use Cases and Risks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful ally in healthcare. From revolutionizing diagnostics to streamlining patient care, integrating AI into healthcare systems promises a future brimming with unprecedented advancements and efficiencies. In this article, we want to discuss the role of AI in the healthcare market.
AI in the healthcare market

Through the application of machine learning algorithms, medical professionals can delve into patient data with unprecedented precision, swiftly identifying anomalies and taking proactive measures to safeguard patient health. Notably, AI-driven systems exhibit remarkable accuracy in scrutinizing medical images, facilitating the prompt diagnosis of diverse conditions, including cancer and diabetes. Moreover, AI facilitates the analysis of genetic data, paving the way for personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patients. One exemplary instance is Google DeepMind groundbreaking initiative, which adeptly identifies ocular diseases by scrutinizing retinal scans.
Innovative AI-based programs are increasingly finding their place in polyclinics, aiding therapists in patient diagnosis. These programs employ neural networks to analyze patient complaints, cross-referencing them with extensive databases comprising millions of patient records. This sophisticated approach enhances diagnostic accuracy, enabling medical professionals to make well-informed decisions promptly.
Furthermore, the landscape of disease prediction has witnessed substantial evolution with the emergence of algorithms capable of forecasting disease occurrences based on comprehensive data analysis. Leveraging electronic medical records, these studies can predict an individual’s susceptibility to various ailments such as diabetes, heart disease, or depression, thus enabling timely intervention and preventive measures.
AI startups in the healthcare industry
The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and healthcare heralds a new era in medical science, empowering early diagnosis and prognosis, thereby enabling the prevention and prompt treatment of numerous diseases at their nascent stages. Below are examples of pioneering AI startups revolutionizing the healthcare landscape:
- IBM Watson for Oncology. Leveraging its formidable analytical capabilities, IBM Watson for Oncology has combed through a staggering 30 billion data points, assisting physicians in selecting optimal cancer treatments by drawing insights from vast pools of medical data.
- Healx. This innovative startup harnesses the power of AI to match drugs in clinical trials with rare diseases, offering hope to patients by accelerating the discovery of potential treatments.
- Arterys. Harnessing the capabilities of cloud computing, Arterys facilitates the dissemination of 4D Flow images to hospital radiologists via web browsers. This revolutionary approach empowers radiologists to make critical, life-saving treatment decisions swiftly and accurately.
- Thymia. Pioneering the use of AI in mental health assessments, Thymia has developed an AI-powered video game that delivers faster, more precise, and objective evaluations. This groundbreaking innovation promises to enhance mental health diagnostics and interventions.
Moreover, AI algorithms are instrumental in analyzing extensive public health data, encompassing insights from social media, news portals, and official statistics. By discerning patterns and trends, these algorithms can predict potential disease outbreaks and epidemics, enabling proactive measures by government agencies to mitigate their impact.
For instance, a system developed by Johns Hopkins University exhibits remarkable prowess in early sepsis detection, outperforming traditional methods by several hours and reducing the likelihood of patient mortality by 20%.
Furthermore, a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute underscores the transformative potential of AI in breast cancer diagnosis. Analyzing mammograms from over 26,000 women, the AI system achieved an impressive accuracy rate of 94.5%, surpassing the traditional accuracy rate of 88.4% for radiologists. This breakthrough holds promise for enhancing breast cancer screening efficacy and saving lives through early detection.
AI use cases in the healthcare industry

Particularly in the realm of surgery, the amalgamation of robotic systems and AI is revolutionizing surgical practices, facilitating intricate procedures with heightened precision and reduced patient risk. Within the operating theater, AI assumes the role of a real-time data analyst, furnishing surgeons with invaluable insights to inform decision-making throughout surgeries. Here are 6 transformative AI applications in healthcare.
Personalized therapy based on genetic information
Harnessing AI’s capabilities, healthcare providers can craft bespoke treatment regimens by leveraging patients’ genetic profiles. This personalized approach enhances treatment efficacy while mitigating adverse effects, thereby maximizing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Drug response prediction algorithms
AI-driven algorithms scrutinize extensive datasets detailing patients’ responses to medications, prognosticating individualized drug reactions. By preemptively identifying potential adverse reactions and optimizing treatment efficacy, these algorithms bolster patient safety and treatment effectiveness.
Improving accuracy and reducing trauma
Robotic surgical systems like da Vinci leverage AI to enhance surgical precision, minimize tissue trauma, and expedite patient recovery. These sophisticated systems execute intricate maneuvers with unparalleled accuracy and stability, translating to superior surgical outcomes and reduced patient morbidity.
3D modeling and surgery planning
AI facilitates the creation of intricate 3D models of patients’ organs derived from medical imaging data. Empowering surgeons to meticulously plan surgeries, anticipate challenges, and mitigate risks, this technology augments surgical precision and diminishes complication rates.
AI-powered assistants
Within the operating theater, AI assumes the role of a proficient assistant, adept at analyzing patient data, monitoring vital signs, and furnishing surgical recommendations. This collaborative synergy between surgeons and AI optimizes surgical decision-making and patient care delivery.
Virtual reality and training
Integrating AI with VR and AR technologies, healthcare professionals can undergo immersive training in a virtual environment prior to real-life surgeries. These cutting-edge training tools equip aspiring physicians and surgeons with invaluable hands-on experience, fostering proficiency and enhancing patient safety during actual surgical procedures.
Want to develop your AI-based product in healthcare? Contact us at OS-System!
Application of AI in healthcare: limitations and risks
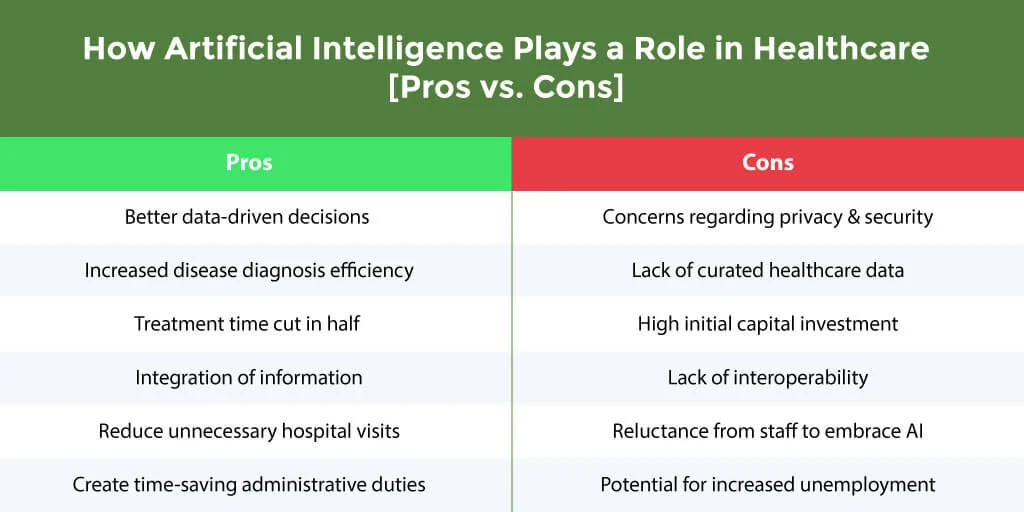
Despite the immense potential, the integration of AI into healthcare confronts several challenges and inherent risks. These include concerns surrounding data privacy and security, as well as the potential for diagnostic or treatment errors stemming from flaws in AI algorithms. Additionally, the seamless integration of new technologies into existing medical systems and the imperative of adequately training staff to leverage these tools pose formidable hurdles.
Outlined below are the primary limitations and risks associated with AI implementation in healthcare:
- Data privacy. As AI processes increasingly sensitive health data, safeguarding patient privacy becomes paramount. The formulation of robust regulations akin to HIPPA is imperative to fortify patient confidentiality and mitigate privacy breaches.
- Lack of accuracy and diagnostic errors. Despite advancements, AI algorithms are susceptible to errors, occasionally resulting in erroneous diagnoses or disease prognoses. Addressing these shortcomings necessitates continual technological refinement and validation.
- Dependence on data quality. The efficacy of AI hinges on the caliber and abundance of input data. Inadequate or subpar data inputs can yield erroneous or perilous conclusions, underscoring the significance of data integrity and quality assurance measures.
- Legal liability. Navigating legal liability in instances of AI-related errors or mishaps remains convoluted, engendering uncertainty and potential risks for healthcare providers. Clarity in legal frameworks is indispensable to mitigate liability concerns and foster accountability.
- Resistance from the medical community. Some healthcare professionals may evince reluctance towards embracing new technologies, apprehensive about the prospect of job displacement, or encroachment upon professional autonomy. Addressing these apprehensions necessitates proactive engagement and stakeholder buy-in.
- Training and adaptation are needed. Efficacious AI integration mandates comprehensive training of medical personnel to harness novel technologies effectively. The acquisition of requisite skills and competencies demands substantial time and resources, underscoring the need for strategic workforce development initiatives.
- Cybersecurity. AI systems are susceptible to cybersecurity threats as they rely on interconnected data networks. Moreover, AI can be weaponized to orchestrate targeted cyberattacks, underscoring the exigency of robust cybersecurity protocols and AI-based defense mechanisms.
Nevertheless, an active introduction of AI in diverse industries will continue.
Conclusion
The trajectory is clear: the pervasive integration of AI into medical practice is poised for exponential growth. With AI at the helm, novel methods for diagnosing and treating diseases are on the horizon, alongside the burgeoning applications of robotic surgery. Moreover, AI stands as a formidable ally in medical research, expediting the development of groundbreaking drugs and therapies. This collective evolution promises to redefine the healthcare industry in manifold ways:
- Reducing research time and costs. AI can revolutionize drug development, curtailing research timelines and costs by prognosticating the efficacy of individual components and optimizing clinical trial processes with unparalleled precision.
- Increasing access to care. The advent of AI-driven telemedicine is beneficial for remote regions grappling with inadequate transportation infrastructure.
- Integration with other technologies. Anticipate a future marked by the seamless convergence of AI with cutting-edge technologies like IoT, blockchain for secure patient data management, and virtual/augmented reality for immersive training and treatment modalities.
- Advancement of preventive medicine. AI’s prowess in early risk detection empowers a paradigm shift towards preventive healthcare, enabling proactive interventions to forestall diseases rather than merely treating them reactively.
If you are looking for a reliable IT partner for your healthcare project, we at OS-System can help. We stand as a distinguished and dependable ally in crafting AI solutions tailored for the medical realm. With our specialized knowledge, proven track record, collaborative ethos, ethical framework, bespoke offerings, and penchant for innovation, we emerge as a steadfast partner for AI initiatives within medicine.
Feel free to contact us to discuss the development of your AI-based medical project.
Subscribe to us










