App Development Stages: 6 Phases to Build Mobile Application
What are the six important steps that make up a mobile app development workflow? We’ll take a closer look at each of them in this post.
Never before has system application and in-app advertising been foreseen to generate a high income. A $693 billion in income for applications in 2021 is unbelievably interesting. Furthermore, by 2022, workplace mobility is predicted to be valued at $510.39 billion.
Although different businesses are attempting to capitalize on this wave, yet some are unaware of how to properly develop an app. These growth estimates can help your firm succeed in the competitive marketplace, but only if they’re backed up by carefully maintained mobile application development phases.
This growth strategy will ensure that your company application development venture is an accomplishment, not even minding the height or complexity of the scheme.
Phases to building a mobile application include:
1. Formulate a Feasible Strategy
The method for changing your understanding into a big program is the main effort in the mobile app development lifecycle. You may make this a bigger element in the entire mobility protocol. It’s important to be aware that each app’s goals vary, hence the mobility technique must be conformed to each phase of the app development workflow.

During this stage, you’ll:
- Determine who the application users
- Examine the competition.
- The intents and aims of the app must be ascertained.
- Assign a mobile outlet for the developed app.
2. Analysis and Planning
The application concept begins to develop at this point, after which it becomes a real mission. Definition of use cases and capture of comprehensive functional codes are the first steps in the assessment and planning strategy.
Create a project plan when you’ve defined the application’s objectives. This entails putting forward and classifying feasible application mandates into landmarks to be delivered. If you’re short on time, resources, or money, create a minimal viable product and highlight it for the preliminary takeoff.
Assessing the talent you’ll require for any application development project is a facet of the preparation policy. Typical phone systems such as iOS and Android tend to use diverse advancement technology packages. If you want to make an application that works with iOS or Android, you’ll be needing software developers that specialize in either iOS or Android on board.
You have to decide on a name for your application. And just like domain names, mobile app names must be distinct for every application in an app store. Review every app store if possible to make sure the app name you’ve got isn’t taken.
Useful article: How to create a mobile app architecture?
3. UI / UX Design
A user-friendly interface is included in the UI/UX layout. The goal of the application product is to create a wholly mobile experience that is intuitive and straightforward to employ.
The accomplishment of a system application is defined by how well potential users perceive and utilize the application’s attributes. The intention of adopting UI/UX to improve a phone application is to produce a unique user experience that is appealing, straightforward, and simple to use. The early stages of development benefit from good interface design.
Information Architecture & Workflows
The very introductory stage in a functional app development workflow that works for mobile is to figure out what feedback an application will show users, what information it will capture, how users will interact with the final product, and how people will drive within the application.
Enterprise mobile applications for businesses include customers with varied responsibilities and rights. It Is crucial to include these regulations in the instructional component of your application. Workflow diagrams aid in the identification of every conceivable engagement a client has with the application.
Wireframes
Illustrations on paper are a common starting point for smartphone application developers. Wireframes are a type of visual illustration. Wireframes, also known as low-fidelity mockups, are semantic blueprints that give graphic display to your application’s functionality.
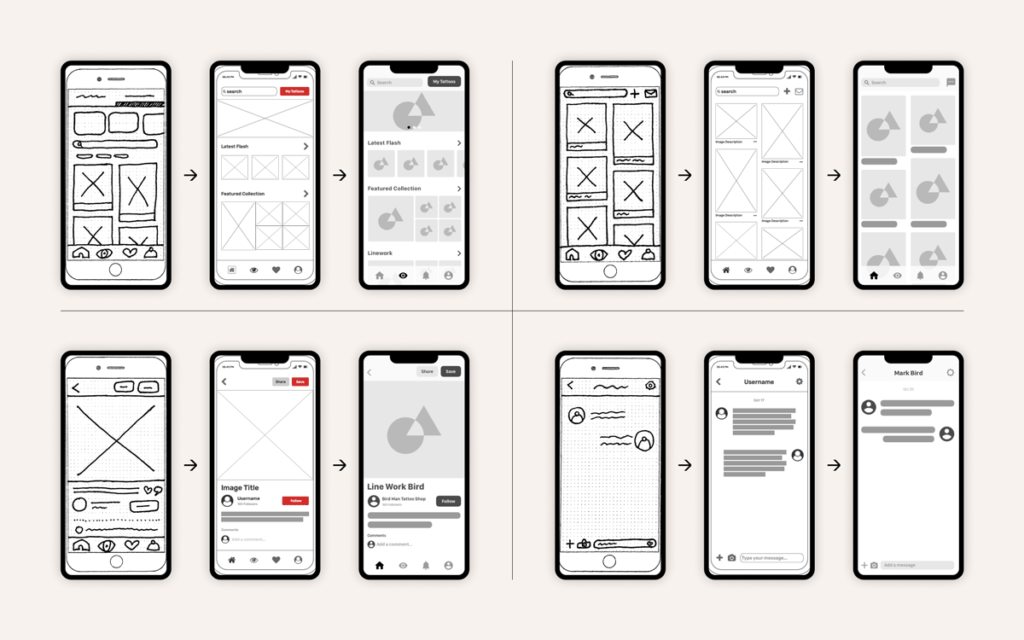
Wireframes are more concerned about aesthetic value and customer experience than with color frameworks and patterns. Wireframes are a simple and affordable way to build app templates and iterate over them during the design evaluation process. When building wireframes, keep the device-specific plan in mind. So it doesn’t matter if your application is utilized on an iPhone, iPad, or Android phone or tablet; it enables straightforward and device-specific mobile usage.
Style Guide
These are dynamic papers that document an application’s building criteria, from a firm’s branding guidelines to navigation symbols.
The guides that have been styled out are:
- Specifying the fonts of the application
- The color pattern of the app
- How will the application to be manufactured represent what an institution stood for
A style management strategy helps you organize an application development. Formulating style guides in the early stages of building an app can help mobile application developers work more efficiently. At the same time, your software will look the same if you follow the style guide. Use the iOS application design standards and Android application development protocols for Android as part of your app structure.
Mockups
An ultimate representation of a program’s illustrated design is known as a high-precision mockup. The information architecture, workflow, and aesthetics of programs will all change as design evolves. Adobe Photoshop is the most widely used program for producing high-quality mockups.
Prototype
To show the capabilities of a mobile application, mockups are employed to have a stationary design. Although employing platforms such as Invision and Figma, you may turn it into a functional prototype. Having prototypes are extremely beneficial for mimicking a program’s user experience and activities that will appear in the final product. Prototyping takes time, but it’s worth it because it allows you to test your program’s design and functionality early on. Changes are frequently identified via prototypes.

When an application’s technical specifications aren’t thoroughly planned out, sometimes organizations choose to do prototypes during the wireframing stage. Alternatively, a focus group may be required to examine the application’s planned features.
4. App Development
Concurrently with the prototype, the foundation stages of building an app are still essential. Before you begin writing your codes, make sure you’ve done this:
- Specify the product backlog
- Select a technology package
- Set application’s building goals
A standard mobile application project consists of three major components:
- Back-end/server technology
- API(s)
- The mobile app front-end
Back-End/Server Technology
The back-end/server technology section contains the database and server-side components required for a mobile application’s enabling features. If you’re utilizing a back-end framework that you already own, you may need to make some changes to accommodate the awaited mobile features.
You may be interested to know which backend languages are popular now.
API
API, an acronym for Application Programming Interface is a way an application communicates with a back-end server or cloud storage.
Mobile App Front-End
Applications front-end are the graphical parts of software that users interact with. It’s normally on the device, or at the very least, the app’s icon is pinned to the device’s applications directory or displayed on the home screen.
Now for the backend, one can utilize practically any web programming language and cloud storage. For designing mobile applications, you must select a tech framework that is compatible with any mobile operating system platform. To make iOS apps, you can make use of Objective-C as the framework or better still consider using Swift. While the most prevalent programming language used to construct Android applications is Java, another efficient one that may be considered is Kotlin.
To develop a phone application, there are a variety of codes and based approaches to choose from; the key is to select the technology platform that is most appropriate for your application.
The modern editions of mobile releases have greatly accelerated the growth of mobile tech. Plus, new mobile equipment hits the store now and then. Skill is important to assembling smartphone applications on time and funding, especially since procedures and gadgets change frequently. If meeting up to demand speedily is your primary goal, use flexible development methods. You can use this method to share software that contains a fully functional program. By setting up advancement phases as part of a flexible development plan, you can clone mobile applications.
Every development stage is sent over to the software testing unit for review and approval.
5. Testing
Examining for quality assurance (QA) is a crucial element of the mobile app development workflow since it ensures the application’s stability, performance, and security. To confirm that your program has been completely assessed, you must write test cases that cover every area of checking the developed application.

Test cases, like use cases, help to manufacture and test smartphone apps. Test samples are utilized to assess software quality by executing the testing process, monitoring repairs, and documenting test results. Involving the quality management team during the computation and setup practice is an excellent practice. Knowing your program’s functionality ideals and goals will aid you in developing precise test cases.
To produce a great mobility result, your application should push through the subsequent testing procedures.
User Experience Evaluation
The actual result has no alternative but to mirror the user experience specified by the application development team, which is a significant move in smartphone application testing. The application’s visual effects, function, and interactivity form a first impression on the end-user. User adoption is significantly influenced by whether or not your software adheres to the original design ideas.
Functionality Evaluation
A well-developed application works efficiently to be successful. It is tough to foresee the character and usage systems of end-users.
To encompass as many assessment scenarios as feasible, the mode of the program should be evaluated by as many users as possible. If two different users try to perform the same function but get different results, you may discover a problem that can come as a surprise. Two users may completely fill a similar form and end up submitting varied data that can bring about malfunctions.
The motive of operating tests is to verify that your application is working properly for clients. It is then divided into system tests (the technique of the program as a whole) and modular tests (operations by certain functions) (each function of the program works normally).
When creating mobile applications for iOS and Android, the function examination should involve a functionality comparison between the two application versions.
Performance Evaluation
For examining the operation of your app, you can try a variety of quantitative parameters.
- How does your program successfully respond to user requests?
- How fast does the program display load?
- Is the software causing a memory leak or a low battery?
- Is your software making the most of your network bandwidth?
- Is your program taking up more space than you think?
Even if your program meets basic performance criteria, check the utilization of your program, APIs, and servers by simulating the maximum number of concurrent users. Even when used quickly, the program should withstand the load and function well.
Security Testing
Security is critical for corporate mobile applications. A hacker assault can be caused by any possible vulnerability. Many businesses hire outside firms to conduct rigorous security tests on their software. Quality and development teams can take a few simple actions to make your software secure.

If a user is required to log in, both the device and the server must keep track of such sessions. If a user’s session has been inactive for a long time, the system should terminate it (typically within 10 minutes for mobile applications). Make sure you’re utilizing a trusted source if your app saves user credentials on the device so they can sign in again. For instance, the iOS application’s keychain feature.
Data entry formats in mobile applications should be carefully examined to avoid the loss of confidential information.
Gadget and Platform Evaluation
Now and then, fresh mobile gadgets with modern equipment, firmware, and technique are listed. Mobile OS is remodeled every few months.
HTC, Xiaomi, Samsung, and Motorola are some mobile gadget manufacturers adopting the Android program, and also set up their devices because Android operates as an open-source. These gadgets are in numerous scopes and structures.
In contrast to Apple’s, Apple owns the hardware and the operating system, so the management environment is more demanding. However, you can use a wide variety of iPhone and iPad (Apple iOS) devices.
Testing while developing a mobile application differs from testing while developing a web-based application. You can only examine web applications on Windows with the Chrome browser. However, to ensure that your mobile application operates smoothly for all users, you need to test it on multiple mobile machines or device simulators.
The organization decided to develop corporate mobile applications for a single mobile platform due to the difficulty of testing all mobile devices, the continuous maintenance costs, and the complexity of managing mobile devices (which often provide users with mobile devices). As a general rule, most businesses develop enterprise mobile apps for Apple’s iOS platform first, and then only when necessary, for the Android platform.
Testing is critical to the long-term performance of a program and is an integral part of the entire mobile application development process. Building a high-quality mobile application requires careful planning of mobile tests.
During the testing stage, there are several options for testers to share application advancement and configuration. For iOS apps, the most common method is to use Testflight, while for Android apps, email or wireless is the preferred method.
6. Deployment & Support
Before launching a successfully built application, it must be proposed and accepted by the application stores or shops such as Google Play Application Store & Apple Application Store for Android & iOS respectively. Before a newly built application for mobile can be released for public use, a developer account for the previously mentioned application stores is required.
The metadata for an application’s publication in the store must include:
- A unique application title
- Personalized application description
- Category the app belongs
- Keywords for easy recognition of the app
- Icon for starting the program
- Screenshots from the Application Store

When an iOS application is uploaded to the Apple App Store, it goes through an evaluation phase that can take anywhere between a few days to several weeks, based on the value of the application and how well it adheres to Apple’s iOS software guidelines. You must provide a trial user profile to Apple as part of the review process especially if your program employs users to log in.
Why Play Market and App Store will remove your app?
Applications for Android do not pass through an evaluation phase and the publishing to the android mobile application market is done within a few hours of being submitted.
Monitor your app’s usage with mobile analytics systems and measure Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to determine its success once it’s released in the app stores. Check crash reports or other user-reported concerns regularly.
Encourage clients to feel free to drop comments and recommendations about your application. To maintain the interests of customers using your application, end-user assistance plus frequent app updates with features will be crucial. Contrary to web applications, which can make patch releases available to app users instantaneously, phone application updates must follow the same submission and review procedure just like the original submission. Furthermore, you must keep up with technological growth and remodel your application regularly to support new mobile gadgets and operating systems.
Final thoughts
Application design is a continuous process that will continue even after the initial release as user input is collected and new features are added. Hopefully, this post has provided you with a better understanding of the mobile app development workflow and its various stages, which range from selecting a partnership and conducting Product Discovery to app delivery and upkeep. Every mobile application that’s been created follows the same development lifecycle. When designing enterprise mobile applications, follow our thoughtful technique.
![]()
Subscribe to us










